Linked List 中我們只能由前往後依序找節點,如果要再往前找需要從頭再掃過一次,這時只要在節點結構加一個欄位記錄前一個節點位置就能往前找。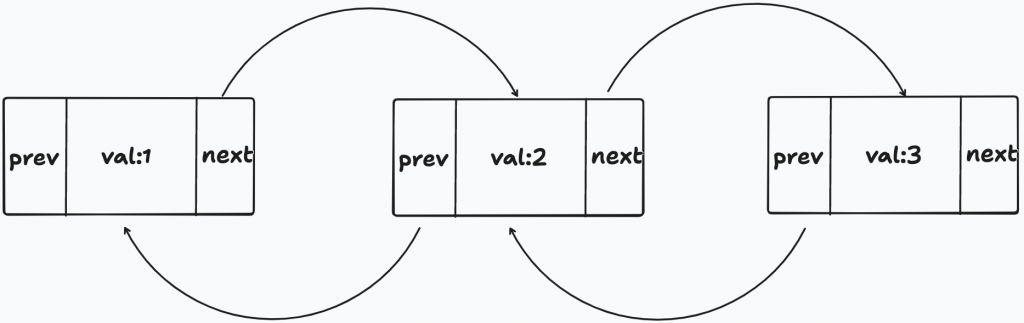
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::{Rc, Weak};
struct Node {
val: i32,
next: Option<Rc<RefCell<Node>>>,
prev: Option<Weak<RefCell<Node>>>,
}
impl Drop for Node {
fn drop(&mut self) {
println!("Drop Node {}", self.val);
}
}
fn main() {
// 建立三個節點
let n1 = Rc::new(RefCell::new(Node { val: 1, next: None, prev: None }));
let n2 = Rc::new(RefCell::new(Node { val: 2, next: None, prev: None }));
let n3 = Rc::new(RefCell::new(Node { val: 3, next: None, prev: None }));
// 串接
n1.borrow_mut().next = Some(Rc::clone(&n2));
n2.borrow_mut().prev = Some(Rc::downgrade(&n1));
n2.borrow_mut().next = Some(Rc::clone(&n3));
n3.borrow_mut().prev = Some(Rc::downgrade(&n2));
// 正向印出
let mut cur = Some(Rc::clone(&n1));
print!("正向: ");
while let Some(rc) = cur {
print!("{} ", rc.borrow().val);
cur = rc.borrow().next.clone();
}
println!();
// 反向印出
let mut cur = Some(Rc::clone(&n3));
print!("反向: ");
while let Some(rc) = cur {
print!("{} ", rc.borrow().val);
cur = rc.borrow().prev.as_ref().and_then(|w| w.upgrade());
}
println!();
}
//正向: 1 2 3
//反向: 3 2 1
//Drop Node 1
//Drop Node 2
//Drop Node 3
Rc<T> V.S. Weak<T>Rc<T>有多個擁有者,每次 Rc::clone() 引用計數(strong_count)+1,如果上面的範例node結構改成都是Rc<RefCell<Node>>,會出現n1指向n2、n2指向n1形成了參考循環,引用計數(**strong_count)**永遠不歸零,物件就不會被釋放,因此需要
next 用 Rc(強引用),因為你通常需要擁有後面的節點。
prev 用 Weak(弱引用),避免形成循環引用導致 memory leak。
必要時使用downgrade將Rc<T>轉成Weak<T>、upgrade將Weak<T>轉成Rc<T>
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::{Rc, Weak};
struct Node {
val: i32,
next: Option<Rc<RefCell<Node>>>,
prev: Option<Rc<RefCell<Node>>>,
}
impl Drop for Node {
fn drop(&mut self) {
println!("Drop Node {}", self.val);
}
}
fn main() {
// 建立三個節點
let n1 = Rc::new(RefCell::new(Node { val: 1, next: None, prev: None }));
let n2 = Rc::new(RefCell::new(Node { val: 2, next: None, prev: None }));
let n3 = Rc::new(RefCell::new(Node { val: 3, next: None, prev: None }));
// 串接
n1.borrow_mut().next = Some(Rc::clone(&n2));
n2.borrow_mut().prev = Some(Rc::clone(&n1));
n2.borrow_mut().next = Some(Rc::clone(&n3));
n3.borrow_mut().prev = Some(Rc::clone(&n2));
// 正向印出
let mut cur = Some(Rc::clone(&n1));
print!("正向: ");
while let Some(rc) = cur {
print!("{} ", rc.borrow().val);
cur = rc.borrow().next.clone();
}
println!();
// 反向印出
let mut cur = Some(Rc::clone(&n3));
print!("反向: ");
while let Some(rc) = cur {
print!("{} ", rc.borrow().val);
cur = rc.borrow().prev.clone();
}
println!();
}
//正向: 1 2 3
//反向: 3 2 1
//沒有drop
Rust collections有實作Doubly Linked List實作,如果可以自定義linked list結構可以使用std::collections::LinkedList來操作push_back、push_front、pop_back、pop_front、append等操作。
#![allow(unused)]
fn main() {
use std::collections::LinkedList;
let mut list1 = LinkedList::new();
list1.push_back('a');
let mut list2 = LinkedList::new();
list2.push_back('b');
list2.push_back('c');
list1.append(&mut list2);
let mut iter = list1.iter();
assert_eq!(iter.next(), Some(&'a'));
assert_eq!(iter.next(), Some(&'b'));
assert_eq!(iter.next(), Some(&'c'));
assert!(iter.next().is_none());
assert!(list2.is_empty());
}
喪我們刷一題練習一下std::collections::LinkedList
題目:想像你開啟一個瀏覽分頁首頁開始依序記錄下你瀏覽記錄,按左上角back可以回到上一頁,forward回到back前的位置,visit會前往新路徑並歸零forward
輸入:
argument1:["BrowserHistory","visit","visit","visit","back","back","forward","visit","forward","back","back"]
argument2:
[["leetcode.com"],["google.com"],["facebook.com"],["youtube.com"],[1],[1],[1],["linkedin.com"],[2],[2],[7]]
輸出:[null,null,null,null,"facebook.com","google.com","facebook.com",null,"linkedin.com","google.com","leetcode.com"]
解法1. 使用Double Link List記錄全部瀏覽記錄,和目前位置,只要有back、forward就更新目前位置,visit先確定目前位置是否是最後一個是的話直接更新,不是的話把後面不需要的node丟掉,剩下的就處理steps有沒有超過邊界[0,list.len()-1]。
new -> [leetcode] size:1 cur:0
visit -> [leetcode, google] size:2 cur:1
visit -> [leetcode, google, facebook] size:3 cur:2
visit -> [leetcode, google, facebook, youtube] size:4 cur:3
back 1 step-> [leetcode, google, facebook, youtube] size:4 cur:2
back 1 step-> [leetcode, google, facebook, youtube] size:4 cur:1
forward -> [leetcode, google, facebook, youtube] size:4 cur:2
visit -> [leetcode, google, facebook, linkedin] size:4 cur:3
back 2 steps -> [leetcode, google, facebook, linkedin] size:3 cur:1
back 7 steps -> [leetcode, google, facebook, linkedin] size:3 cur:0
use std::collections::LinkedList;
struct BrowserHistory {
list:LinkedList<String>,
size:usize,
cur:usize
}
impl BrowserHistory {
fn new(homepage: String) -> Self {
Self {
list:LinkedList::from([homepage]),
size:1,
cur:0
}
}
fn visit(&mut self, url: String) {
if(self.size==self.cur+1){
self.list.push_back(url);
self.size = self.size+1;
self.cur = self.cur+1;
} else {
while(self.size-1!=self.cur){
self.list.pop_back();
self.size-=1;
}
self.list.push_back(url);
self.size = self.size+1;
self.cur = self.cur+1;
}
}
fn back(&mut self, steps: i32) -> String {
self.cur = (self.cur as i32 - steps).max(0) as usize;
self.list.iter().nth(self.cur).unwrap().clone()
}
fn forward(&mut self, steps: i32) -> String {
self.cur = (self.cur as i32 + steps).min(self.size as i32 -1) as usize;
self.list.iter().nth(self.cur).unwrap().clone()
}
}
解法2:還記得stack講到的undo、redo可以用2個stack存上一步後下一步嗎,剛好可以用來解這題,用back向量來記錄瀏覽歷史紀錄,如果有回到上一頁,把記錄放到forward向量,當回到下一頁時可以去拿,跟解法1一樣需注意邊界,back向量最少一定要放首頁。
struct BrowserHistory {
back:Vec<String>,
forward:Vec<String>,
}
impl BrowserHistory {
fn new(homepage: String) -> Self {
Self {
back:Vec::from([homepage]),
forward:Vec::new(),
}
}
fn visit(&mut self, url: String) {
self.back.push(url);
self.forward.clear();
}
fn back(&mut self, steps: i32) -> String {
for i in 0..steps.min(self.back.len() as i32 -1) {
let Some(forward) = self.back.pop() else { break};
self.forward.push(forward);
}
self.back.last().unwrap().to_string()
}
fn forward(&mut self, steps: i32) -> String {
for i in 0..steps {
let Some(back) = self.forward.pop() else { break};
self.back.push(back);
}
self.back.last().unwrap().to_string()
}
}
Weak<T>弱引用避免循環引用std::collections::LinkedList 用法介紹